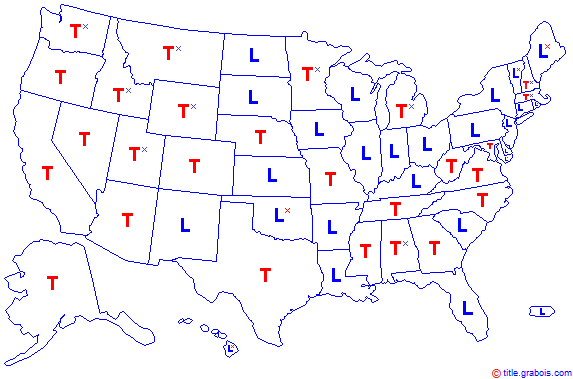
In a Title State, the lending institution holds title to the property in the name of the borrower through a Deed of Trust. In a Lien State, the deed stays with the borrower (mortgagor), and the lender (mortgagee) places a lien on the property using the mortgage instrument. Generally, foreclosure in Title States occurs through a non-judicial proceeding, while Lien States are conducted via judicial methods; it varies with each state.